
By changing the DNS settings and selecting a server that doesn’t include the domain in a blacklist, you can open the relevant website as desired.This convenient setup works well as long as the DNS Servers of your service provider are working well and have the capacity to handle DNS queries generated by its users. In this case, name resolution will not be performed and you will be denied access to these websites. DNS blocking: The DNS filter list of the provider’s name server may contain domains you wish to access.This is usually due to a temporary problem that can be solved straight away by changing DNS servers, without having to wait for a solution from the provider.
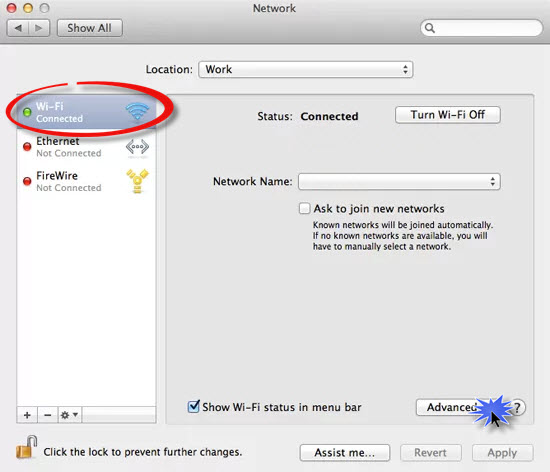
 Availability: The DNS server may not be available, which stops name resolution in its tracks and prevents websites from loading. Tools like namebench help you to find the quickest DNS server for you. Here, many users prefer OpenDNS name servers as well as Google’s public DNS servers, which are considered particularly fast. Speed: Another DNS server may offer a speed advantage in name resolution, resulting in faster loading times and a better ping in online games. However, changing the standard DNS server may be necessary or advisable for the following three reasons: Since the providers are interested in delivering the best possible service, they usually also provide the required capacity to respond to incoming DNS queries quickly and reliably. Typical DNS connection points are the name servers of the various internet providers, which are generally a good choice. Simply connect the devices you wish to use to the router protocols like DHCP will then handle the allocation of the information you need in order to connect.
Availability: The DNS server may not be available, which stops name resolution in its tracks and prevents websites from loading. Tools like namebench help you to find the quickest DNS server for you. Here, many users prefer OpenDNS name servers as well as Google’s public DNS servers, which are considered particularly fast. Speed: Another DNS server may offer a speed advantage in name resolution, resulting in faster loading times and a better ping in online games. However, changing the standard DNS server may be necessary or advisable for the following three reasons: Since the providers are interested in delivering the best possible service, they usually also provide the required capacity to respond to incoming DNS queries quickly and reliably. Typical DNS connection points are the name servers of the various internet providers, which are generally a good choice. Simply connect the devices you wish to use to the router protocols like DHCP will then handle the allocation of the information you need in order to connect. 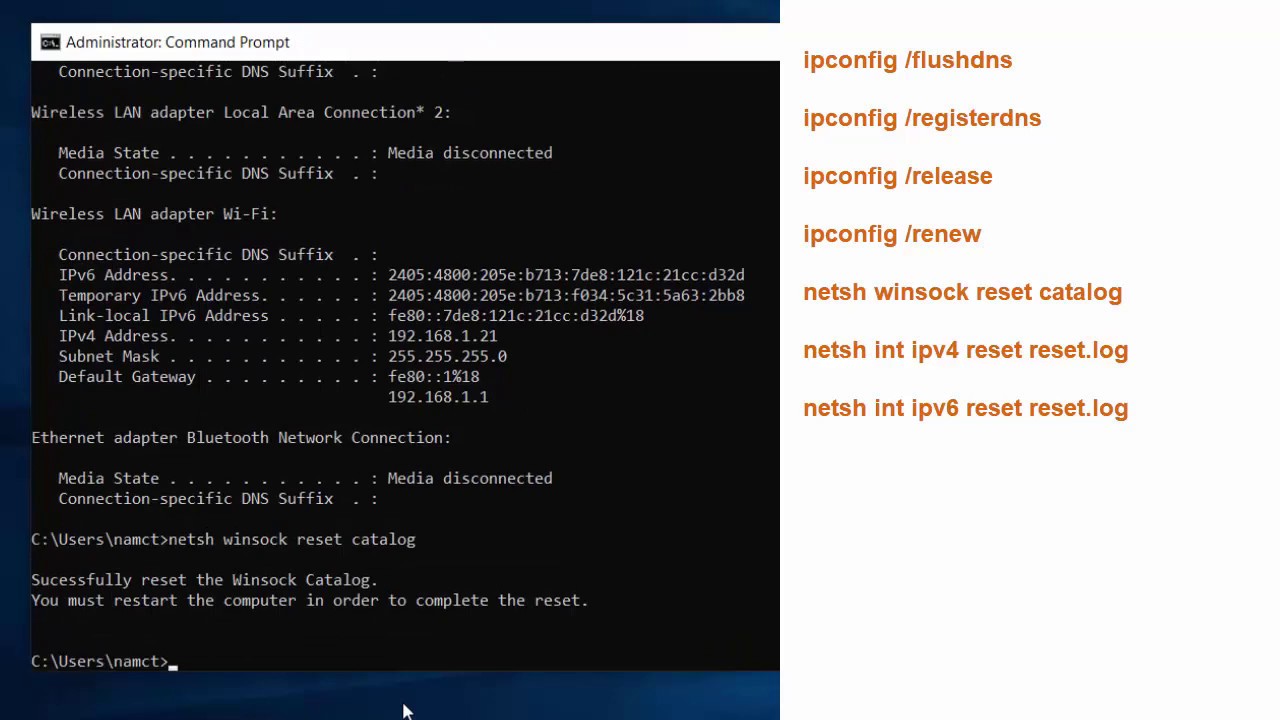
As a user, this means you don’t need to deal with configuring your own address and ensuring name resolution yourself. When connecting to the internet via a router, you automatically obtain not only the IP address but also the DNS server settings.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
